For all referrals and consultations, please call 1300 832 667 (1300 VECMOS). You will be connected directly to ARV and an ECMO Specialist to assist you.
ECMO should be considered whenever a young patient (< 65 years of age) acutely deteriorates with potentially reversible cardiac and/ or respiratory failure despite optimal conventional treatment. The patient should ideally be identified and referred before the onset of secondary organ failures, as the risk of death rapidly increases beyond this point.
In general, only hospitals with in house ECPR programs can consider ECMO for patients in cardiac arrest. There might be exceptions to this in case of accidental hypothermia and selected toxicology cases where prolonged CPR times are warranted.
Referrals for patients above 65 are welcome, but enduring patient benefit following ECMO in this older age group is less likely and use must be highly targeted. In general, the use of ECMO for severely shocked or arrested patients in this age group is not advisable. ECMO may be useful and successful when applied as an anticipated peri-procedural support for high risk procedures in this age group.
For all referrals to the Victorian ECMO Service and available to all hospital staff considering ECMO support for their patient: Call 1300 VECMOS (1300 832 667)
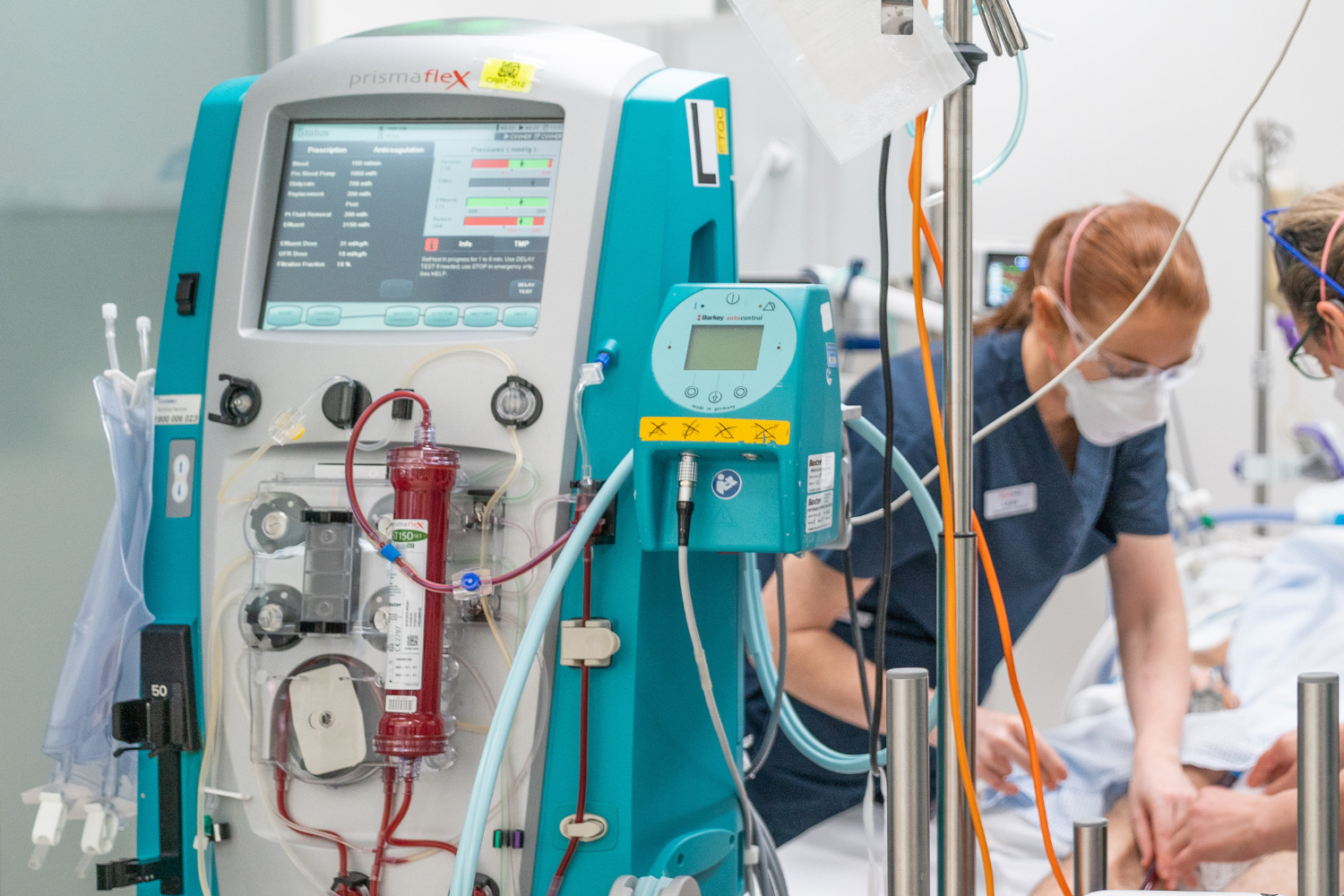
VECMOS Retrieval Administration Support Officers (RASO) are the first point of contact for all referrals as they will receive and process all Victorian ECMO Service consultation and coordination calls and connect required staff.

Once a decision is made to retrieve a patient, the composition of the retrieval team required is determined both by the stability of the patient and the tier of the referring hospital.
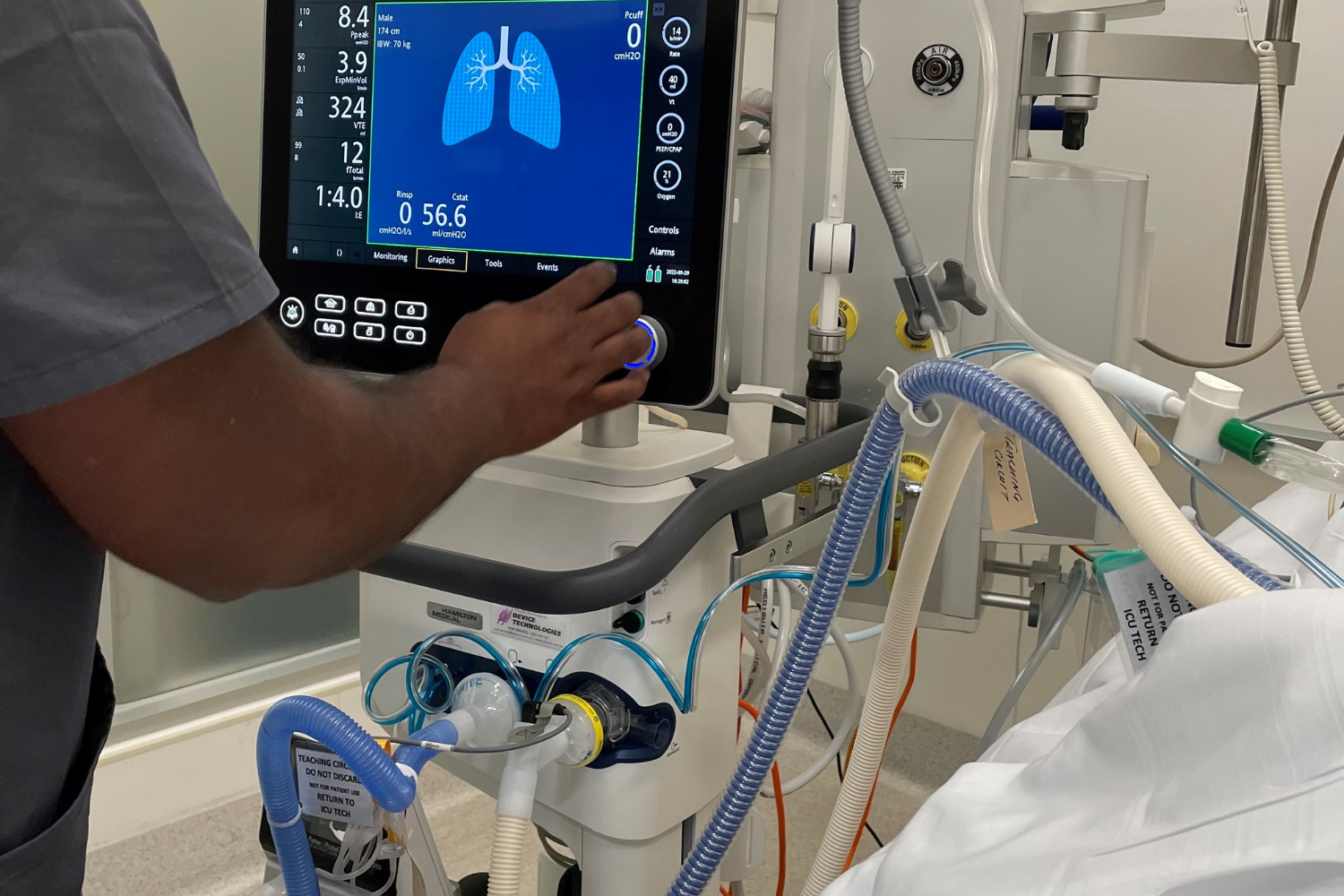
Individual case selection for ECMO initiation is seldom straightforward and evaluation should be as thorough as permitted by the clinical setting.

The Mode of ECMO is defined by where ECMO circuit blood is drained from the patient, where it is returned to, and the resulting physiological effects.

The prevention of complications is fundamental to successful ECMO care and there are a number of fundamental precautions to prevent common and severe complications.